
Faced with an abundance of new data on acute urinary retention, urologists need to reach a consensus about the risks of urinary retention this may promote movement toward patient centered prevention strategies with tailored treatment options. In addition, elevated post-void residual urine volume (PVR) has. Conclusions: Clinicians are adopting less invasive approaches (eg pharmacology or catheterization) to treating patients who present with the symptoms, sign, and condition of urinary retention. and a correlation between urinary incontinence and bacteriuria has been reported 1/3.
#URINARY RETENTION POST VOID RESIDUAL TRIAL#
Clinical trials on the short-term use of antimuscarinics have not provided evidence that these agents increase the risk of retention data on longer term administration are needed. To confirm urinary retention To identify incomplete bladder emptying To assess post void residual urine volume In a trial without catheter (TWOC), to prevent. α-Receptor antagonists and 5α-reductase inhibitors may be useful in preventing urinary retention episodes and progressive benign prostatic enlargement. The gold standard assessment of post-void residual urine. However, age, previous retention episodes, lower urinary tract symptoms, chronic inflammation, serum prostate specific antigen level, prostate size, and urodynamic variables appear to be predictors of acute urinary retention. Background: Postoperative urinary retention occurs in 17 to 42 of Radical hysterectomy (RH) cases.
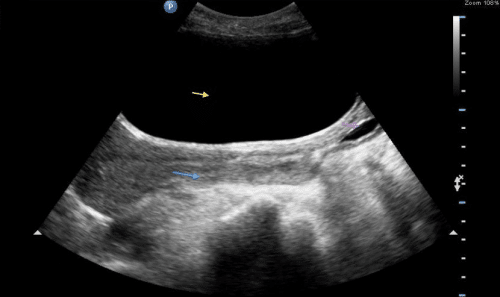
Community based studies and clinical trials in patients with benign prostatic enlargement and/or lower urinary tract symptoms yield different estimates of the incidence of retention and only provide information on the epidemiology of acute urinary retention. Many factors can contribute to the development of retention, including bladder outlet obstruction, detrusor underactivity, and neurogenic bladder conditions. Use of this term to describe a symptom, a sign, and a condition further complicates the issue. Results: The term urinary retention lacks precise clinical or urodynamic meaning. Articles not directly relevant to urinary retention or post-void residual urine were excluded. In the older client, it is thought to be a common finding. Materials and Methods: A MEDLINE® search for articles written in English and published before April 2007 was done using a list of terms related to urinary retention. There is a low risk of acute urinary retention using an alpha-blocker and an antimuscarinic drug in men known to have a post-void residual urine volume of less than 150 mL. Post void residual urine is defined as the volume of urine left in the bladder at the end of voiding. We reviewed several aspects of urinary retention that require clarification with the objective of stimulating discussion among urologists to establish an accurate and coherent definition of urinary retention and significant post-void residual urine, and clarify risk factors. Moreover, the definition of significant post-void residual urine is unclear.

Standardized criteria have not been established and many questions remain unanswered. Purpose: The definitions of acute and chronic urinary retention remain empirical and subject to wide interpretation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
